The requirement of reliable protection of a person from the damaging effects of electric current has always been ahead of the capabilities of science and technology in creating protective devices that meet this goal. Today, innovative developments in the electrical industry fully meet all the criteria for devices of this type. The article reveals the question of such a device as an RCD: what it is, its purpose, principle of operation, choice and application.

Means and methods of electrical protection: modern devices and features of their work
As soon as the use of electric current entered our lives, it immediately became necessary to protect against its damaging effects on human health. First of all, it is the insulation of the conductive parts of the wiring and parts of the current receivers.

But complete isolation is impossible, as in any electrical circuit there are technological breaks and contact groups. There is always the likelihood of violation (destruction) of the insulating layer of conductive elements and their mechanical damage, and most importantly, statistical regularity in violation of safety, instructions and operating rules of electrical equipment, both at the production and household level.
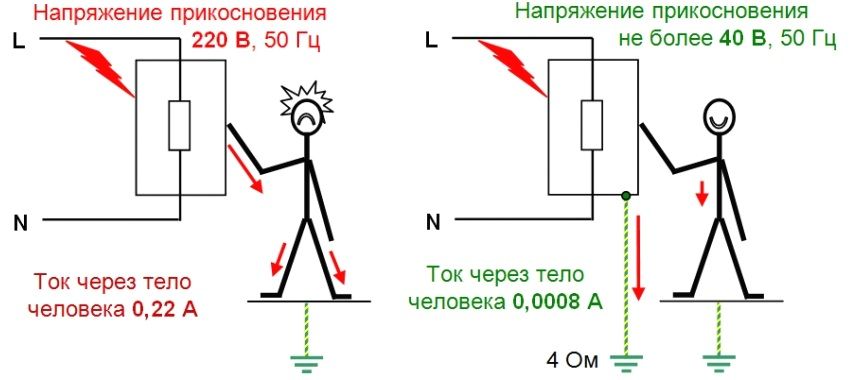
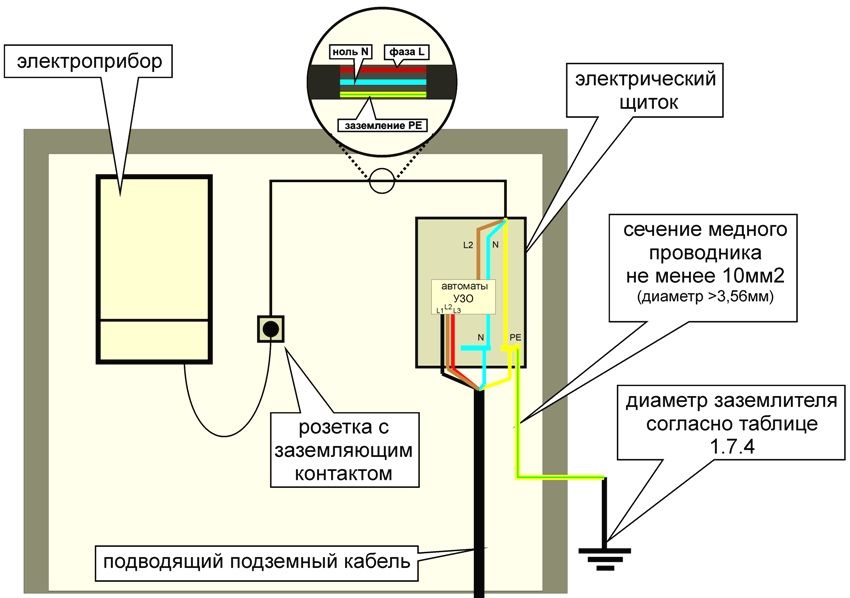
One of the most effective ways to protect against the damaging effects of electric current is the organization of the ground loop. The ground loop is an artificial conductor connection with the “ground” (the so-called PE-conductor) of neutral conductive housings or parts of electromechanisms, having a resistance not exceeding 4 ohms. The listed items of electrical equipment may be energized due to a short circuit on the body of the phase conductor or lightning current.
The main purpose of the ground loop device is to exclude the possibility of electric shock to a person or an animal in case of contact with the body or part of the electrical equipment mechanism, which is energized due to the short circuit of the phase electric current.
Note! In AC networks with a grounded neutral and a voltage of up to 1 kV (this is the format of the housing power supply), grounding as the main protection against electric shock caused by indirect contact does not apply, since it is not effective.
The problem of the most effective protection against the effects of electricity on humans was decided by the so-called differential current devices (UDT) – this is a large segment of control and protection devices for various purposes and design features. The classification of the UDT segment is quite extensive: from the control method, the type of installation and the number of poles, to the possibility of regulation and the time delay of the tripping differential current.
Consider what is RCD. The acronym for this abbreviation is a safety device. Requirements for the installation and use of UDT are given in the supplementary editions of PUE – rules for the installation of electrical equipment and in a series of standards for electrical installations of buildings IEC 60364 and the effects of current on humans and livestock IEC 60479-1.
Innovator in the development of the USO was Germany. The first valid sample protection device was designed and manufactured in the thirties of the last century. The leakage current sensor used the smallest possible differential current transformer, and the control element used a polarized magnetic relay with a sensitivity of 100 milliamps (mA) and a response time of no more than 0.1 second.
The threshold for fixing the differential current in the prototype was about 80 mA. A control relay with a sensitivity of less than 80 mA was impossible to develop at that time due to the lack of materials with the required electromagnetic characteristics. And only in the middle of the twentieth century was proposed a new constructive solution of the RCD. The design took into account mechanisms to eliminate false positives from discharges during a thunderstorm and significantly increased the sensitivity of the differential current to 30 mA.

Also, the dimensions of the RCD have changed: from the size of the parcel box to the modern format that can be installed on a DIN-rail in modern electrical cabinets.
Technical experts in the field of electrical and electronic developments are already making predictions for the future. They firmly believe that soon such systems as protection against electric shock will be managed by artificial intelligence.
He will be able to perform not only measuring and monitoring functions, but also carrying out video and audio monitoring of the object given to him, make instant decisions on any random situations and, if necessary, alert rescue services.
Among the most popular of the protective UDT, working in living conditions, include protective disconnect devices (UZO). The RCD operates as a human protector against electric shock and as a preventive mechanism to prevent accidental ignition of wiring cables and electrical equipment cords.

The functional idea of the device under consideration is based on the laws of electrical engineering, which postulate the equality of the incoming and outgoing current in closed electrical circuits with active loads.
This means that the current flowing through the phase conductor must be equal to the current flowing through the neutral conductor – for single-phase circuits with two-wire wiring and that the current in the neutral conductor should be equal to the sum of the currents that flow in the phases for the three-phase four-conductor circuit.
When a person accidentally touches the uninsulated parts of the conductive circuit elements in this circuit or when the exposed part of the wiring comes in contact (due to damage) with other conductive objects that form a new electrical circuit, the so-called current leakage occurs – the equality of the incoming and outgoing currents is violated .
This violation can be registered and used as a command to turn off the entire electrical circuit. This process was designed RCD. And within the framework of electrical engineering, the “leakage” current has been called differential current.
The RCD can detect very small “leakage” currents and act as a switch mechanism. Theoretically, the principle of operation of an RCD is as follows (where Iin – input current of the neutral wire, Iout – output current of the phase wire):
- Iin = Iout (system balance without violation, RCD in standby state);
- Iin > Iout (the balance of the system is broken, the RCD detects the appearance of a differential current and turns off the power supply).
When an RCD is installed in the power supply network, this means that protection is provided against:
- the circuit of the phase wire to the body of the appliance. In a large number of cases, these are the heating elements of washing machines, water heaters and heaters. Moreover, breakdown can occur only when the thermal element is heated under the influence of current;
- Incorrect wiring when unscrupulous electricians fix a “twist” of wires in plaster without using a junction box. If the wall is wet – a differential current will leak into the wall from this twist and the RCD will de-energize the line all the time until the plaster dries completely or the connections are properly repaired;
- improper installation in the electrical panel, when seemingly small but “useful” changes made to the circuit change the current distribution and lead to a loss of high efficiency of the device. This will be discussed in more detail later.
The RCD can be triggered for reasons not conspicuous from the first inspection of the connection scheme of household appliances. If you use a gas stove with electric arson gas, or the washing machine is connected by a hose in a metal case to a water tap, or when the neighbors are grounded to the water supply or heating system, then an electrical leakage will again occur, which will trigger RCD. In such cases, a scrupulous engineering analysis is required.
Rules very often have exceptions. This principle has not bypassed the universal qualities of the considered protective device.
The RCD will not react when a person or an animal is energized, but no earth fault current will occur. Such a case is possible when touching simultaneously to the phase and neutral conductor, which is under the control of the RCD, or with full isolation with the floor. The protection of the RCD in such cases is completely absent. The RCD cannot distinguish between an electric current passing through the body of a person or an animal from the current flowing in the load cell. In such cases, safety can be ensured by measures for mechanical protection (complete insulation, dielectric housings, etc.) or complete de-energization of the appliance before its technical inspection.

RCD, which is completely dependent on the supply voltage suitable for the network object, is in working condition only if the indicated network is fully operational. The situation can become dangerous when “above” the RCD breaks the neutral wire, and the phase wire remains energized. Then in the wiring phase wire may become a factor of electric shock, and the RCD due to its own incapacity will not be able to turn off the power to the network.
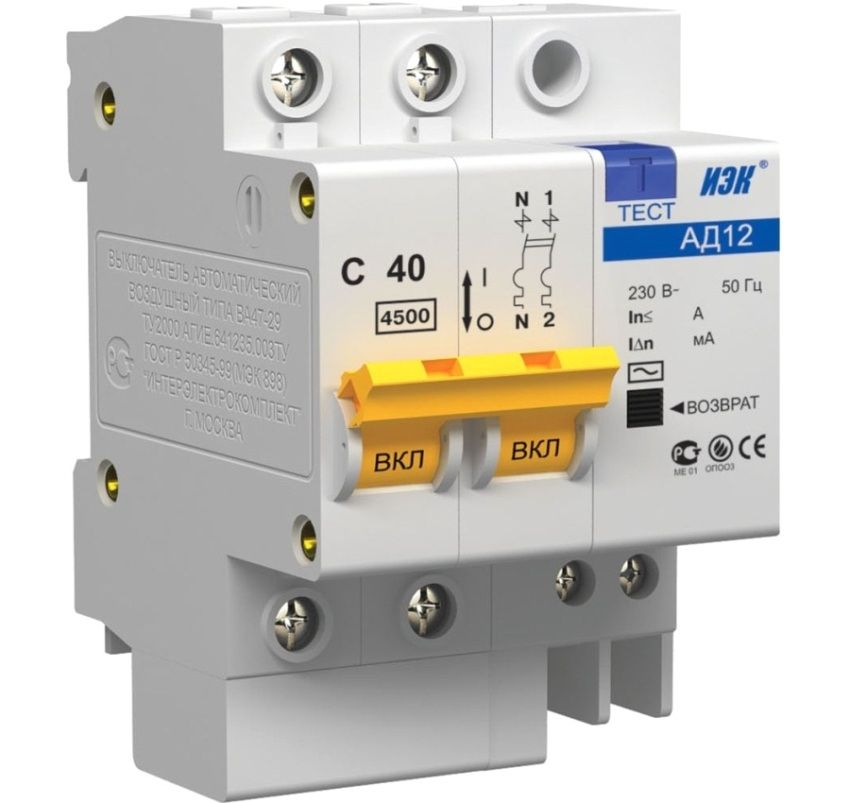
The RCD can “hang” in the standby state if the main contact rod sticks to the solenoid or if the secondary winding of the control device fails and does not work at the right time. In order to check the operating state of the RCD, there is a test mechanism. If you regularly test the device (and to do this, simply press the “T” button – test), the risk of breakdown of the RCD will have a minimum probability.
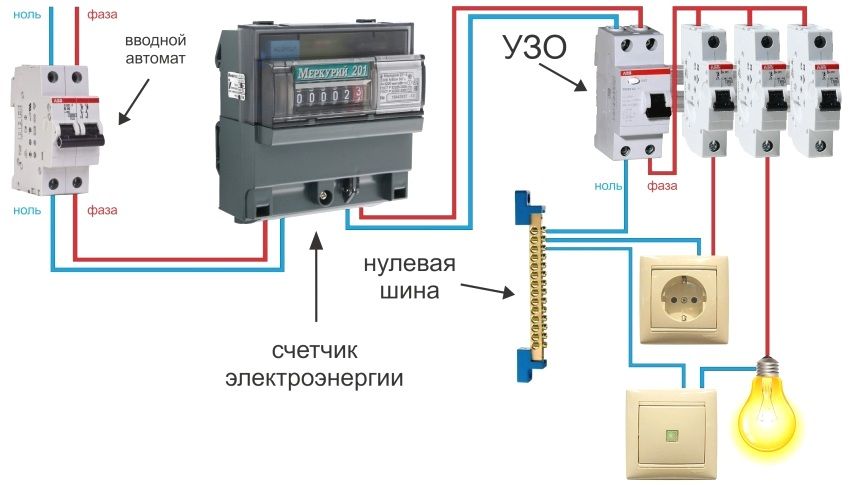
The main use in domestic conditions UZO received when using in electrical groups of bathrooms, kitchens and sockets groups of a large number of connected appliances and equipment. This does not mean that it does not make sense to use RCDs on a common incoming network. This sampling scheme is dictated only by the speed of management and marketing expediency, since RCDs for small currents are much cheaper for the price of devices with more power.
However, in some cases, if we consider hostels, clubs, etc., it will be more reliable to use a general selective RCD due to the massive and simultaneous use of virtually all elements of electrical equipment. A selective-type residual current device differs from the usual one by a long delay time of the tripping differential current (ie, the response time) and is one of the most used devices. When a conventional local RCD is triggered in any circuit, the general selective RCD does not disconnect all wiring immediately, but allows the power supply to be stopped only for a specific group.
For example, if the insulation of the equipment breaks down at the disco and the case (say, the amplifier) is in contact with the phase conductor, then when the operator touches the amplifier, the local RCD triggers and disconnects only the amplifying equipment group, and the selective general RCD does not disconnect all power and such Groups like common lights, toilets and cafes will work in standard mode.
The mechanism of connecting the RCD in the existing network is similar to connecting the circuit breaker with the only difference that when a single-phase circuit breaker requires two terminals to be tightened, then the RCD has four.
If when a person touches a bare portion of a wire or a case of equipment that is under phase voltage, electricity is instantly turned off, then the RCD has tripped.

Important! In AC systems, additional protection via RCDs should be provided for socket groups with a rated current of up to 20A (washing machines, boilers, stoves, etc.) and mobile (portable) equipment and power tools with a rated current of up to 32A, which is used outdoors.
The physical processes occurring in the mechanisms of operation of many modern electromechanical or electronic devices may be completely incomprehensible to us. Not every person has knowledge of engineering and technical disciplines and, naturally, is not able to understand and describe the physical basis of the principles of operation of this or that device. But the principle of use (rules of operation), built on the elements of safety, makes it possible to use the most complex inventions in our daily life.
However, the RCD does not respond to the phenomenon of a short circuit in the wiring circuit and to an excess of current in the circuit. In this connection, it is necessary to install the device together with an automatic switch (“automatic”), which reacts to short circuit and overload on power.
The most important thing is to always follow the safety rules and caution when working with electrical appliances and equipment. As often as possible, visually inspect the open current-carrying elements of electrical wiring and the connected elements of current collectors.

